Response types
Status codes
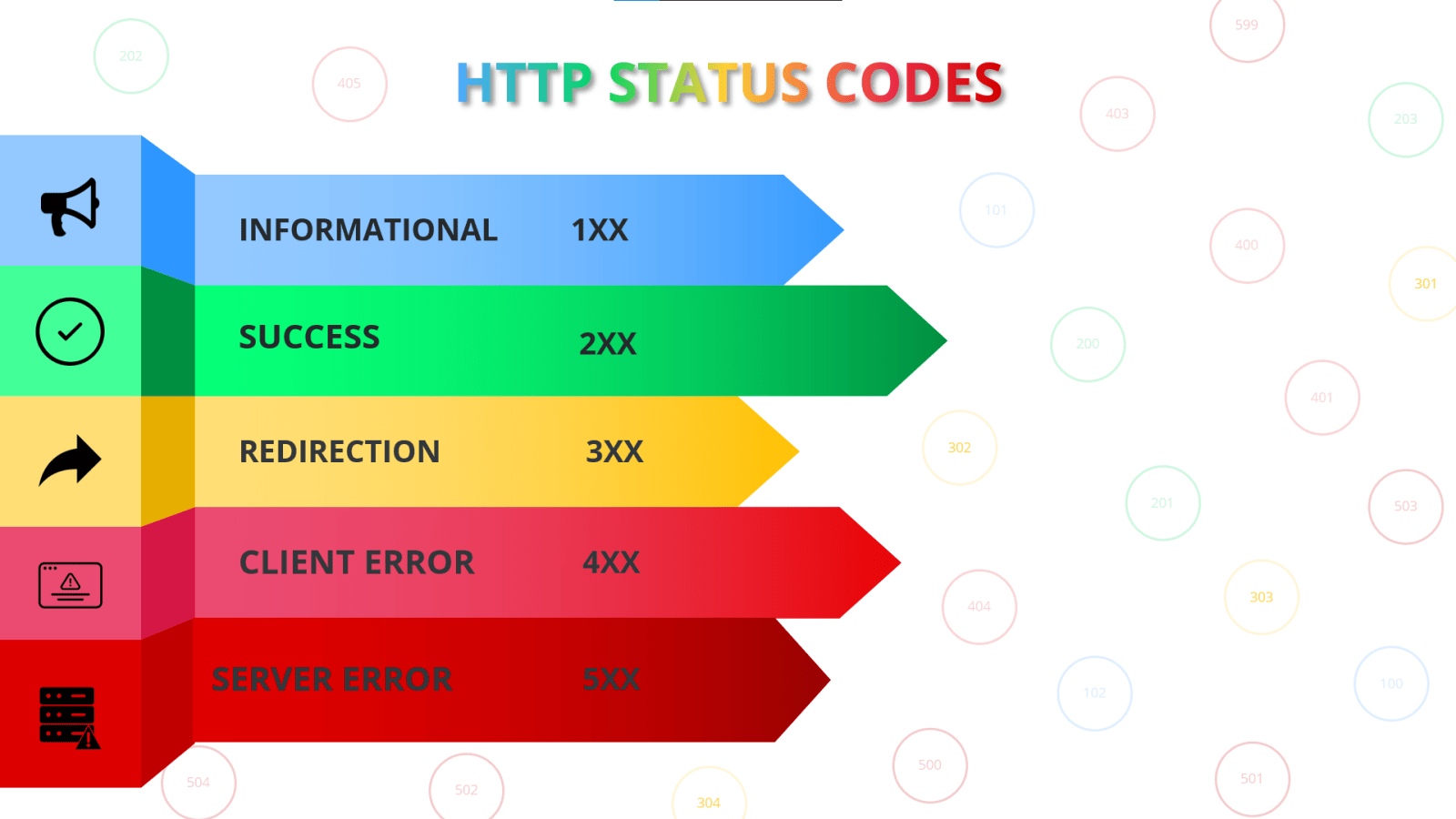
HTTP response status codes indicate whether a specific HTTP request has been successfully completed. Each group contains a lot of different responses, on this page you will find an overview of the most common HTTP status codes. Responses are grouped into five classes: informational responses, successful responses, redirects, client errors, and server errors.
Status messages
The message that accompanies a server status response code doesn’t matter to clients. Most clients rely only on the status code ‘number’ itself. A message should be seen as a recommendation and it is not required the client should examine them.
The status message may differ by HTTP version or even between different RFC documents for the same HTTP version. And with the introduction of HTTP/2, the protocol does not contain a status message or reason at all.
Informational responses
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response.
Successful responses
Status codes indicate that the server successfully processed the request.
| Code | Message | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | OK | The server successfully processed the request. Generally, this means that the server provided the requested page. |
| 204 | No Content | The server sent a valid reply to a client request that contains header information only (i.e., does not contain any message body). Web clients can use this status to process server responses more efficiently, avoiding refreshing pages unnecessarily, for example. |
Redirection messages
Further action is needed to fulfill the request. Often, these status codes are used for redirection.
| Code | Message | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 301 | Moved Permanently | The requested page has been permanently moved to a new location. When the server returns this response, it automatically forwards the requestor to the new location. The response should also include this location. It tells the client to use the new URL the next time it wants to fetch the same resource. |
| 302 | Found / Moved Temporarily | The server is currently responding to the request with a page from a different location, but the requestor should continue to use the original location for future requests. |
| 304 | Not Modified | The requested page hasn’t been modified since the last request. When the server returns this response, it doesn’t return the contents of the page. |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect | The server is currently responding to the request with a page from a different location, but the requestor should continue to use the original location for future requests. There is very little difference between a 302 status code and a 307 status code, but you can use both to temporarily point users to another URL. This status code has the same semantic as the 302 Found HTTP response code, with the exception that the user agent must not change the HTTP method used. |
| 308 | Permanent Redirect | This means that the resource is now permanently located at another URI, specified by the Location: HTTP Response header. This has the same semantics as the 301 Moved Permanently HTTP response code, with the exception that the user agent must not change the HTTP method used. |
Client error responses
These status codes indicate that there was likely an error in the request which prevented the server from being able to process it.
| Code | Message | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request | The server didn’t understand the syntax of the request. |
| 401 | Unauthorized | The request requires authentication, before a resource can be accessed, the client must be authorized by the server. The server might return this response for a page behind a login. |
| 403 | Forbidden | The server is refusing the request. Unlike a 401 unauthorized response, authenticating will make no difference. |
| 404 | Not Found | The server can’t find the requested page. For instance, the server often returns this code if the request is for a page that doesn’t exist on the server. |
| 408 | Request Timeout | The request you sent to the website server (e.g. a request to load a web page) took longer than the website’s server was prepared to wait. In other words, your connection with the website “timed out”. |
| 410 | Gone | The server returns this response when the requested resource has been permanently removed. It is similar to a 404 (Not found) code, but is sometimes used in the place of a 404 for resources that used to exist but no longer do. If the resource has permanently moved, you should use a 301 to specify the resource’s new location. |
| 429 | Too Many Requests | The client has sent too many requests in a given amount of time (“rate limiting”). |
Server error responses
These status codes indicate that the server is aware that it is on error or is incapable of performing the request.
| Code | Message | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | Internal Server Error | The server encountered something it didn’t expect and was unable to complete the request. |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | The server received an invalid response from another server. |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | The server is currently unavailable (due to a server overload or because it’s down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state. |
| 504 | Gateway Timeout Error | The server did not receive a timely response from another server that it was accessing while attempting to load the web page or fill another request by the browser. In other words, 504 errors usually indicate that a different computer, one that the website you’re getting the 504 message on doesn’t control but relies on, isn’t communicating with it quickly enough. |